|
|
|
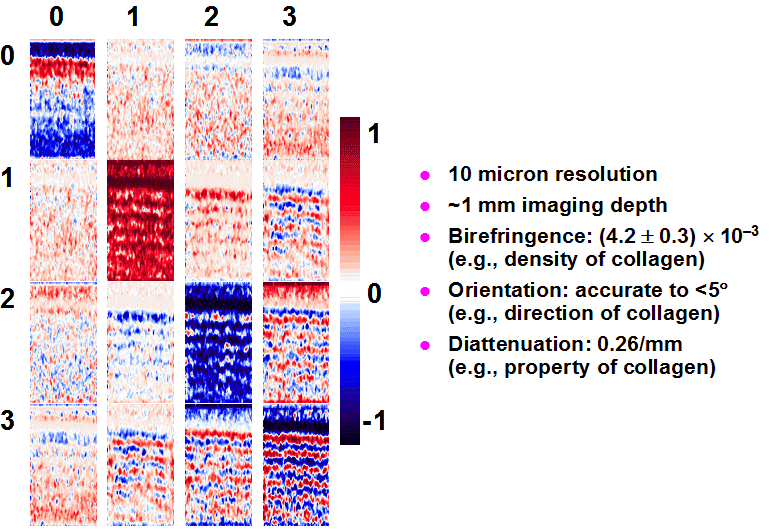
Mueller Matrix Optical Coherence Tomography
|
Mueller matrices provide a complete characterization
of the optical polarization properties of biological tissue. A polarization-sensitive
optical coherence tomography (OCT) system has been built and used to investigate
the optical polarization properties of biological tissues and other turbid
media. The apparent degree of polarization (DOP) of backscattered light
was measured with both liquid and solid scattering samples. The DOP maintains
a value of unity within the detectable depth for the solid sample, whereas
the DOP decreases with the optical depth for the liquid sample. Two-dimensional
depth-resolved images of both the Stokes vectors of the backscattered light
and the full Mueller matrices of biological tissue were measured with this
system. These polarization measurements revealed tissue structures that
are not perceptible with standard OCT.
Selected publications:
-
Li, L.; Maslov, K.; Ku, G.; Wang, L. V.; "Three-dimensional combined photoacoustic and optical coherence microscopy for in vivo microcirculation studies," Optics Express 17(19) 16450-16455 (2009) [PDF]
-
Li, L.; Wang, L. V.; "Optical coherence computed tomography," Applied Physics Letters 91(14) 141107-(1-3) (2007) [PDF]
-
Ai, J.; Wang, L. V.; "Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: removal of autocorrelation using an optical switch," Applied Physics Letters 88(11) 111115-(1-3) (2006) [PDF]
-
Jiao, S. L.; Yu, W. R.; Stoica, G.; Wang, L. V.; "Optical-fiber-based Mueller optical coherence tomography," Optics Letters 28(14) 1206-1208 (2003) [PDF]
-
Jiao, S. L.; Wang, L. V.; "Two-dimensional depth-resolved Mueller matrix of biological tissue measured with double-beam polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography," Optics Letters 27(2) 101-103 (2002) [PDF]
-
Yao, G.; Wang, L. V.; "Two-dimensional depth-resolved Mueller matrix characterization of biological tissue by optical coherence tomography," Optics Letters 24(8) 537-539 (1999) [PDF]
-
Yao, G.; Wang, L. V.; "Monte Carlo simulation of an optical coherence tomography signal in homogeneous turbid media," Physics in Medicine and Biology 44(9) 2307-2320 (1999) [PDF]
|
|

