SPHEREx Near-Infrared Telescope Calibration
Noise Reduction Methods for Large-scale Intensity-mapping Measurements with Infrared Detector Arrays, (ApJS 268, 44, 2023)
We developed specialized readouts and analysis methods for the SPHEREx mission that allow us to achieve large-scale noise stability with Teledyne H2RG detector arrays. The low-noise ASIC Video8 amplifier sampled each of the 32 detector outputs continuously in sample-up-the-ramp mode with interleaved measurements of a stable reference voltage to remove current offsets and 1/f noise from the amplifier. The amplifier addresses rows in an order different from their physical arrangement on the array, modulating temporal 1/f noise in the H2RG to high spatial frequencies. We also developed noise model for the H2RG and Video8 to optimize the choice of parameters.
Cryogenic focus measurement system for a wide-field infrared space telescope, (Applied Optics 63, 3453, 2024)
We describe a technique for measuring focus errors in a cryogenic, wide-field, near-infrared space telescope. The measurements are made with a collimator looking through a large vacuum window, with a reflective cold filter to reduce the background thermal infrared loading on the detectors and optics. We characterized the wavefront error from the vacuum window and cold filter with an autocollimating microscope. For the 200 mm diameter aperture 𝑓/3 SPPHEREx telescope, we achieve a focus position measurement with a ∼15µm systematic and a ∼5µm statistical error.
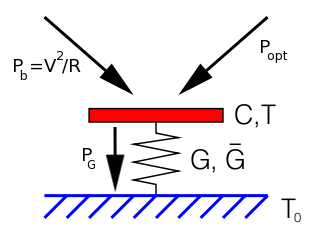
Ultra-low NEP Far-Infrared Detector Development
High-sensitivity transition-edge-sensed bolometers: Improved speed and characterization with AC and DC bias, (Journal of Applied Physics 134, 9, 2023)
We demonstrate the fabrication and characterization of these devices, highlighting their exceptional thermal properties and sensitivity. By optimizing the bolometer's design and integrating it into a compact cryogenic platform, we achieve significant advancements in detecting faint terahertz signals with unprecedented resolution. This work showcases the potential of transition-edge sensors in bolometric applications but also underscores their relevance in future advancements in far-infrared imaging and spectroscopy.

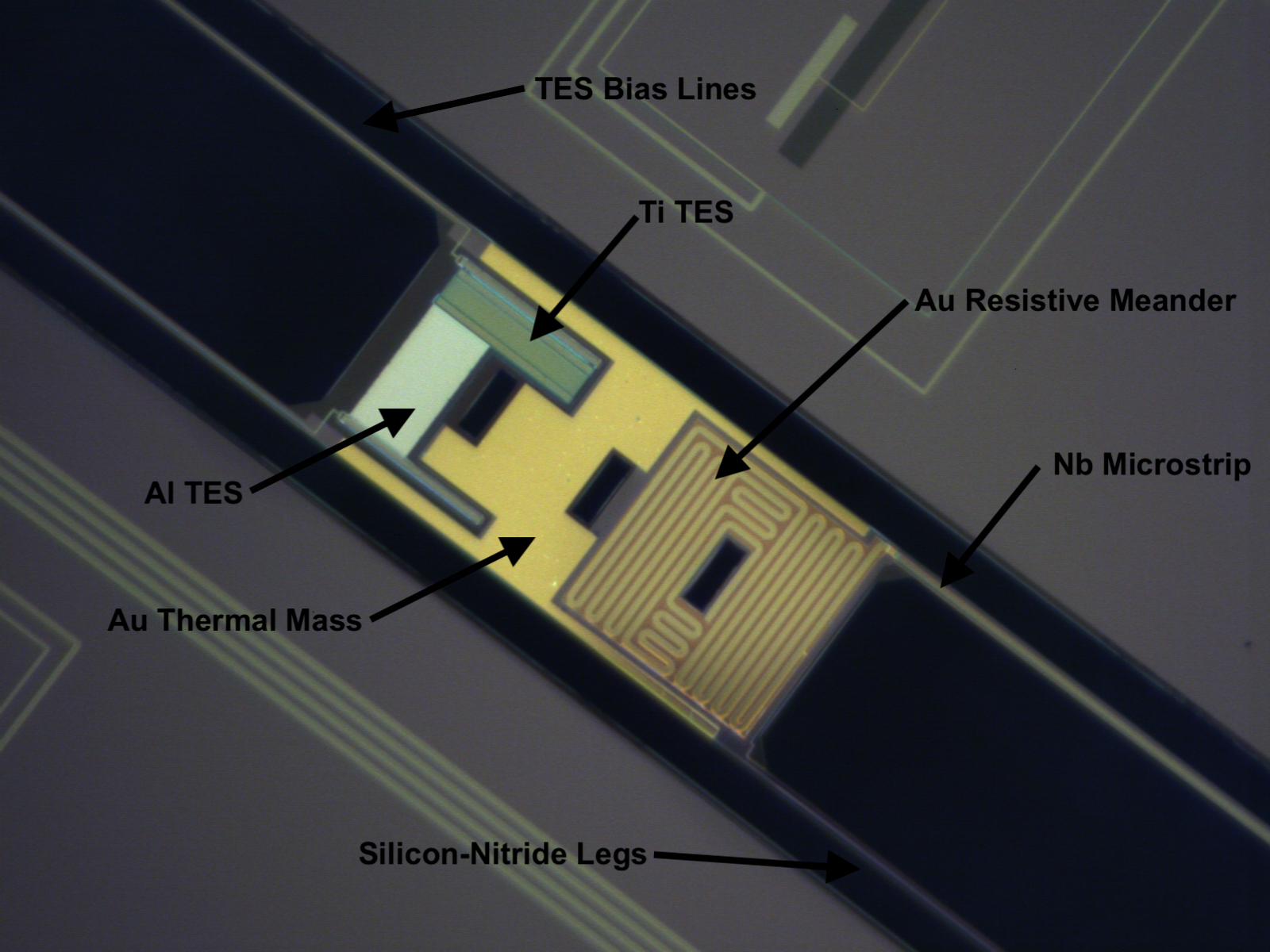
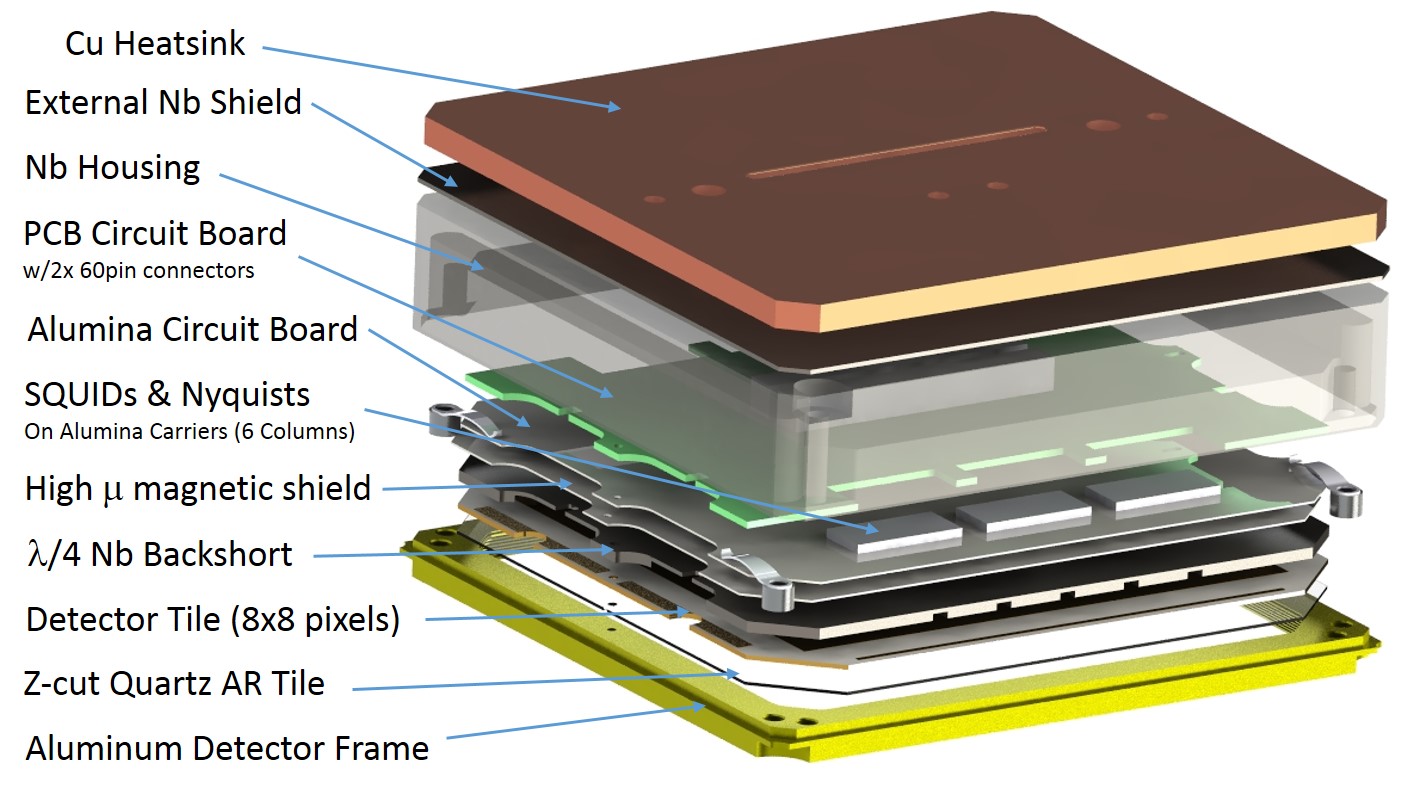
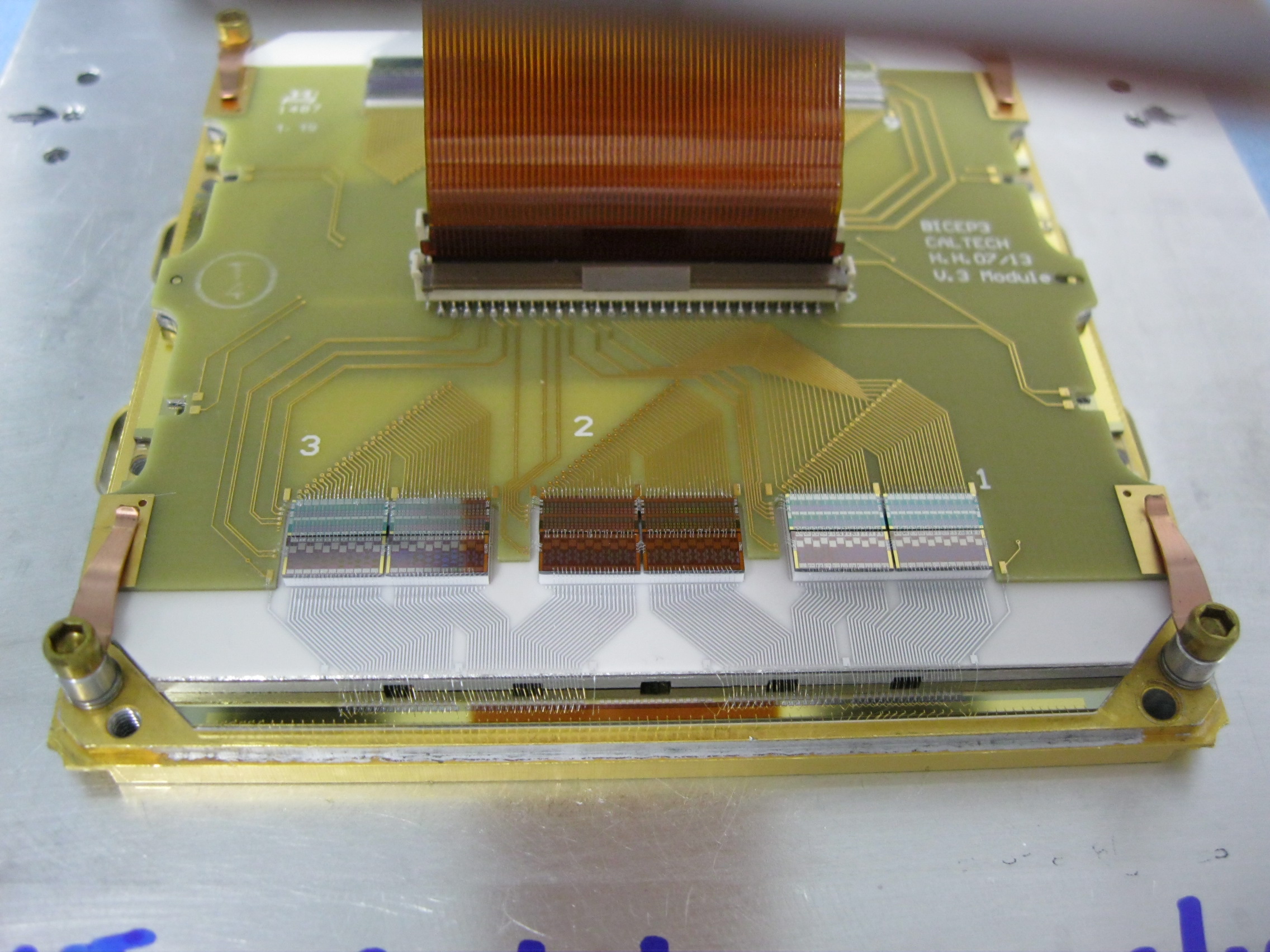
BICEP3 Instrument Developement
Bicep/Keck XV: The Bicep3 Cosmic Microwave Background Polarimeter and the First Three-year Data Set, (ApJ 827, 77, 2022)
BICEP3 has 2560 detectors, fabricated onto 20 silicon tiles, each housed 128 polarization sensitive transition-edge sensors. We use a modular packaging design of detector tile and readout hardware on the focal plane. It is constructed to provide the necessary thermal stability, magnetic shielding and mechanical alignment to operate the detectors, while at the same time allow us to replace individual tile without affecting the well-performed, existing one.
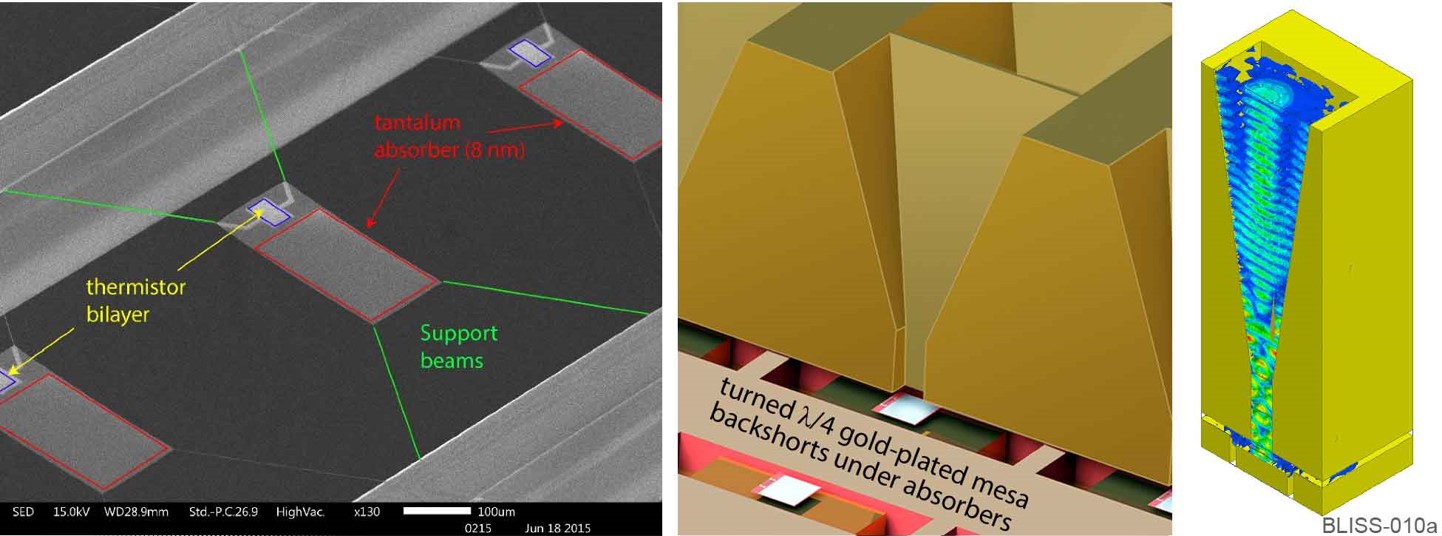
Antenna-coupled Transition Edge Sensors
Antenna-coupled TES Bolometers used in BICEP2, Keck Array, and SPIDER, (ApJ 812, 176, 2015)
We use Transition Edge Sensors (TES) bolometer in all of the telescopes in BICEP/Keck. These are thin films of superconducting metal sputtered onto a released structure in weak thermal contact with the rest of the instrumet only through mildly conducting legs.